Source: digitalvidya
While the headlines have been dominated by the venture capital funding of startups, the unicorn valuations and billion-dollar exits of unicorns, they do represent a smaller side of the startup ecosystem. Behind the scenes of the venture capital boom, another type of startup revolution is quietly happening: startups in India that create crores of revenue without ever receiving venture capital funding.
These startups are not concerned with hitting a value number; they are concerned with generating actual revenue/breaking even and being a profitable business; many of these companies have had the same steady increase since they started, building their brands and cultivating loyal customers for 10 years or longer without taking on any outside financing whatsoever, and in many cases, the business model worked so well for these startups that it wasn’t even necessary for them to attract venture funding to sustain their business model.
The true success stories of Indian bootstrapped startups, how they created sustainable business models, and lessons learned by founders, economicbeacons professionals, and future entrepreneurs on how to build a bootstrapped business in India are the focus of this article.
What Does “Making Crores Without Funding” Really Mean?
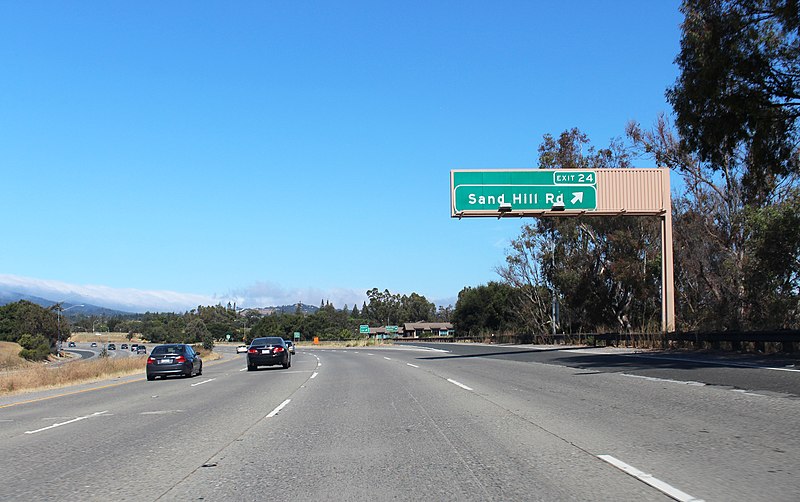
When we say a startup is “making crores without funding,” we are saying the company has grown without receiving investment from venture capitalists or angel investors, or private equity funds. In other words, the startup’s growth came from the following sources:
- Revenue generated from customers
- Reinvestment of internal profits
- Careful cost management
- Long-term business thinking
Startups that bootstrap often reach revenues of between ₹10 crore and ₹8,000+ crore annually while also remaining profitable each year.
Bootstrapping generally allows founders to maintain ownership of their vision and the ability to make their own decisions.
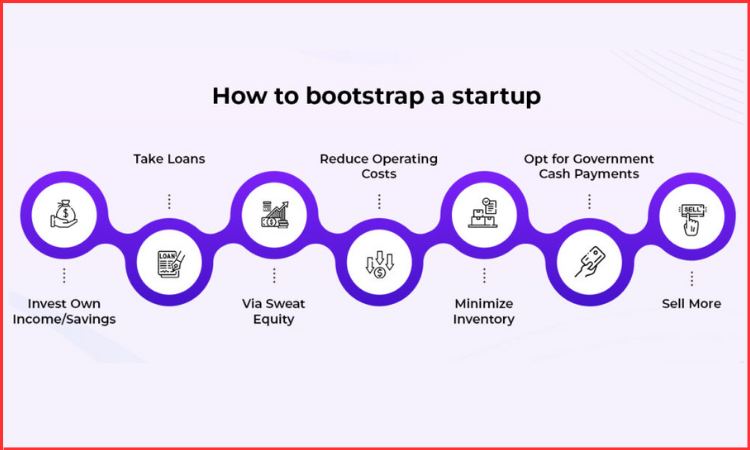
Why Bootstrapped Startups Are Succeeding in India
Source: kiwitech
India is an excellent location for companies to begin “bootstrapped” companies, as it provides the opportunity for business growth by allowing companies to start at a low level, test new ideas, and quickly gauge demand to grow their existing customers.
Most Supportive factors for bootstrapped growth
1) There are many opportunities in India because of its large population and the need for companies to provide products across multiple price points (premium to mass).
2) The cost of doing business in India is significantly lower than in other developed countries, especially when comparing the technology and services industry.
3) Indian consumers are very price-conscious and are willing to pay for quality and trust. Successful businesses in India deliver the above qualities.
4) An increasing number of Indian founders are using a profit-oriented business model, instead of a “burn more cash” model, as a result of understanding the risks of the overfunding model.
Top Indian Startups Making Crores Without Funding (2025–2026)
| Startup | Industry | Founded | Revenue Scale |
| Zoho | SaaS | 1996 | ₹8,000+ crore |
| Zerodha | Fintech | 2010 | ₹6,500+ crore |
| BrowserStack | DevTools | 2011 | ₹1,000+ crore |
| Wingify (VWO) | SaaS | 2009 | ₹300+ crore |
| MapmyIndia | Mapping & IoT | 1995 | ₹300+ crore |
| Vahdam Teas | D2C FMCG | 2015 | ₹150+ crore |
| Perfios (early years) | Fintech SaaS | 2008 | ₹100+ crore |
| Tally Solutions | Accounting Software | 1986 | ₹1,000+ crore |
Zoho: The World’s Largest Bootstrapped SaaS Company

Source: kachwanya
Sridhar Vembu founded Zoho, which has often been described as India’s counterpoint to the Silicon Valley ecosystem, but without the financial backing of venture capitalists found in Silicon Valley.
From the very beginning, Zoho turned down VCs and concentrated its efforts on creating cheap, enterprise-grade applications that could meet the needs of international customers.
Zoho’s strategic plan for growth was based primarily on developing in-depth products over the long term, instead of aggressively marketing any single product or service. To further drive customer loyalty, Zoho developed a full suite of applications, including CRM, accounting, human resources, and collaboration tools, within one complete system.
As of now, millions of users from across the globe utilize Zoho’s applications as tangible proof that bootstrapped businesses can achieve great levels of global success.
Zerodha: Profit-First Fintech That Changed Indian Investing

Source: metastory
In India, the stock trading landscape has changed thanks to Zerodha’s introduction of a low-cost, straightforward model for brokerage fees. Rather than investing a lot of money in advertising, Zerodha put its energy into educating its customers, creating an easy-to-use product, and establishing trust.
Zerodha established itself as profitable very quickly by creating an efficient company using technology and a low operating cost. The company founders are 100% owners of the largest brokerage platform in India.
Zerodha proved that you do not have to come close to bankruptcy to serve as an example of how fintech startups can achieve great things while maintaining their focus on efficiency.
BrowserStack: Developer Tools Built on Customer Love
Source: whippy
BrowserStack addressed a very narrow market need for cross-browser testing; instead of creating many different types of products, it instead concentrated on developing one core solution to perfection.
Sustained growth was achieved through the developer community, referral traffic, and enterprise adoption rather than relying on paid advertising. Revenue generated from sales to enterprises was continually reinvested back into both building the foundation for its global expansion and improving its own products, creating steady growth worldwide.
The success of BrowserStack illustrates that companies focusing on niches can be immensely profitable.
Wingify (VWO): Sustainable SaaS Through Subscription Revenue

Source: indianstartupnews
Wingify is the creator of VWO, a platform for the optimization of website and user experience by large, multinational companies. The business focused first on growing a recurring revenue model based on subscriptions, which allowed for more predictable income streams.
Through early focus on serving global customers, Wingify was able to earn foreign currency whilst based in India, allowing for greater margins on its operations. This approach enabled the company to consistently increase profitability every year with no dilution of shareholders.
MapmyIndia: Building Deep-Tech Without External Pressure

Source: inc42
It took MapmyIndia decades to build the country’s digital mapping infrastructure, unlike most consumer tech startups that have fast business models and ramp up high-speed growth. MapmyIndia’s long game with public institutions (government) and enterprise-based products (automakers, etc.) paid off. MapmyIndia is now one of the largest players in the map-based space (navigation, logistics, smart mobility), demonstrating how a deep tech startup can achieve their goals through disciplined entrepreneurship and strategic vision.
Vahdam Teas: A D2C Brand Powered by Storytelling

Source: inc42
Vahdam Teas bridged the gap between Indian tea growers and international buyers through direct connections and communication. The company has an emphasis on high-quality products, ethical sourcing, and a well-developed narrative about how it all came to be.
Instead of rapidly growing its business through excessive spending, Vahdam has instead worked to lower its cost of goods sold and enhance its profits by concentrating on selling directly to customers. This proves that D2C businesses have the potential to grow globally without the requirement of a large amount of financial backing.
Common Traits of Profitable Bootstrapped Startups
These businesses exhibit a consistent pattern regardless of industry:
- Clear understanding of customer needs and how their product addresses those needs;
- Emphasis on creating great unit economic systems;
- Focused marketing approach;
- Long-term thinking by the founders; and
- Strong focus on maximizing operational efficiency.
Bootstrapped vs Funded Startups: Strategic Differences
| Criteria | Bootstrapped | Funded |
| Decision Speed | Independent | Investor-driven |
| Profit Pressure | Immediate | Often delayed |
| Growth Style | Sustainable | Aggressive |
| Ownership | 100% founder-led | Diluted |
| Risk Level | Lower | Higher |
Is Bootstrapping the Right Choice for Every Founder?
Source: bizzi
The process of bootstrapping a business is not as simple as it appears. It takes time, commitment, and perseverance. However, for entrepreneurs who prioritize maintaining control of their business and creating a stable and sustainable income over time through entrepreneurship, bootstrapping can provide the greatest returns on investment.
Given the current climate of uncertainty and increased expectations from investors regarding profitability and sustainable business practices, bootstrapped start-ups are in a more favorable position for future success than funded start-ups.
Conclusion
Many Indian startups have achieved significant success without outside investment. These business success stories provide an alternative definition of success in entrepreneurship by placing importance on developing customer trust, profitable revenue growth, and disciplined financial management over escapism.
As the startup marketplace continues to develop, making a profit will become a strict requirement for companies in order for them to succeed. These profit success stories are not isolated examples; they represent where the future of the Indian startup company landscape lies.
FAQs
Q1) Is it possible for a bootstrap company to become a unicorn?
Yes, however, it is uncommon but there are some examples e.g. Zoho, of how a company can scale and be independent at the same time.
Q2) Do investors prefer to invest in profitable startups?
Yes, with the focus on revenue visibility and unit economics becoming more important than previously focusing on rapid expansion.
Q3) What types of sectors in India are best suited to bootstrap a company?
The best types of sectors are SaaS, Fintech Tools, Service Sector, D2C and B2B Platforms because they all have a good chance of bootstrapping to success.
Q4) Does bootstrapping progress more slowly than raising capital?
While bootstrapping may take longer to create initial growth, in terms of long-term sustainability, bootstrapping is much stronger.
Q5) What is the primary benefit of bootstrapping a startup company?
The largest advantage of bootstrapping is that the entrepreneur has complete control of the business and can build it without external pressures or influences.



